EHS competency mapping for industries
The synergistic relationship between safety and an organization is something that cannot be overlooked, and safety needs to be integrated into its fabric. EHS professionals build this relationship, and with best practices, ensure that everything falls in place.
To achieve EHS excellence, industries should aim to:
- Facilitate business competitiveness
- Provide functional excellence
- Safeguard human and natural resources
In an organization, competencies are seen as qualifiers to perform certain tasks. Their assessments mean measuring one’s skills, knowledge, traits, behavior and attitude. Competency mapping is performed on a comprehensive level, where one determines the nature and scope of the specific job role, the skills needed (to accomplish), knowledge required, and the behavioral approach necessary to apply those skills and knowledge.
Mapping the core competencies at the every stage of career progression is important.
In health and safety, a well-done competency map links employees to job duties, job duties to hazards and hazards to training to eliminate or mitigate those hazards. EHS roles and responsibilities, stitched within, strengthen the ability of an organization to address EHS risks and maintain quality and quantity of EHS resources.
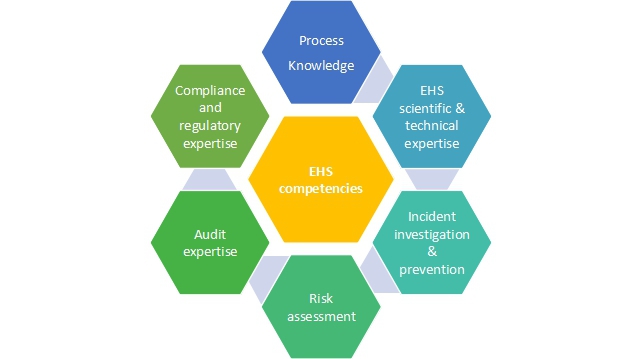
JSA and JHA act as aggregators of safety information and help the safety professionals to draw inferences. This includes the work description, type of wearables to perform the work, potential hazards (if any), any regulatory obligations to be maintained and other such considerations.
The mapping process of EHS professionals produce a database where information is segregated as:
- Associated activities
- Potential hazards or their environmental impacts
- Competencies required to mitigate
- Trainings to be deployed for those identified competencies
With this data, a training matrix, if created, enables the individuals to obtain right trainings at a right time. The primary aim of competency mapping is using well-defined competencies that are in-line with the business priorities and relevant to each person’s role level. Safety professionals use the database produced as a metric against which each individual is selected, developed and fairly evaluated.
EHS Software modules act as pillars for a company’s sustainable future and make the safety systems useful and powerful. Here, checklists of all processes, methods, knowledge, skills and experience are designed to reach objectives. The data consolidated onto a software can then tackle the mapping process systematically.
With modules such as Change management, Safety observation and CAPA, safety professionals can make data-driven decisions and this is a more structured approach to the whole system. Similarly, if an industry maintains a digital version of occupational health, it is easy to access the physical and mental well-being of their employees.
Such software tools, if a part of an industry, can interact with each other, gather relevant information and it becomes easy for EHS personnel to visualize the organization’s existing situation and make decisions accordingly. When different departments jointly coordinate with each other, software modules act as primary tools for recording, reporting and analyzing.
When considered in-premise, software modules generate efficiency benefits for the competency mapping process, where key capabilities are logged and underlined. The potentially overwhelming conditions enable the safety experts to monitor, interpret the rich data and translate them into action.
This is the age of continuous connection, and to stay ahead of the competition, connected strategies need to be fundamental to the industry. The better the company understands its competencies, the more it holds the potential to customize the conditions in its favor.


